What Effect Does Sympathetic Nervous System Stimulation Of The Heart Have On Cardiac Output?
What effect does sympathetic nervous system stimulation of the heart have on cardiac output?. Heart rate is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions beats of the heart per minute bpm. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. The acute phase is aimed at treating the congestion and supporting cardiac output.
Dopamine constitutes about 80 of the catecholamine content in the brain. Parasympathetic Nervous System PNS. Sympathetic Nervous System SNS and.
At the beginning of exercise there is a depression of the PNS and stimulation of the SNS which causes a rapid increase in. The PNS is mainly responsible for managing homeostasis and SNS is mainly responsible for causing action such as the fight or flight response. Therefore incremental dosing is necessary.
Because clinicians and investigators have long observed that factors affecting primarily the venous side of the circulation can have profound influence on cardiac output mechanisms governing the flow of blood to the heart. Venous return refers to the flow of blood from the periphery back to the right atrium and except for periods of a few seconds it is equal to cardiac output. Treatment of congestive heart failure in dogs can be divided into two phases.
Recent clinical reports and animal research suggest that these cardiovascular changes are more likely to occur after unintended intravascular injection of bupivacaine. Factors that play an important role in the. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor.
The heart rate can vary according to the bodys physical needs including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide but is also modulated by a myriad of factors including but not limited to genetics physical fitness stress or psychological status. As a result hypoxemia typically results in a fall in systemic vascular resistance SVR and increased sympathetic input both of which lead to increases in stroke volume heart rate and cardiac output. Dopamine DA a contraction of 34-dihydroxyphenethylamine is a neurotransmitter that plays several important roles in cells.
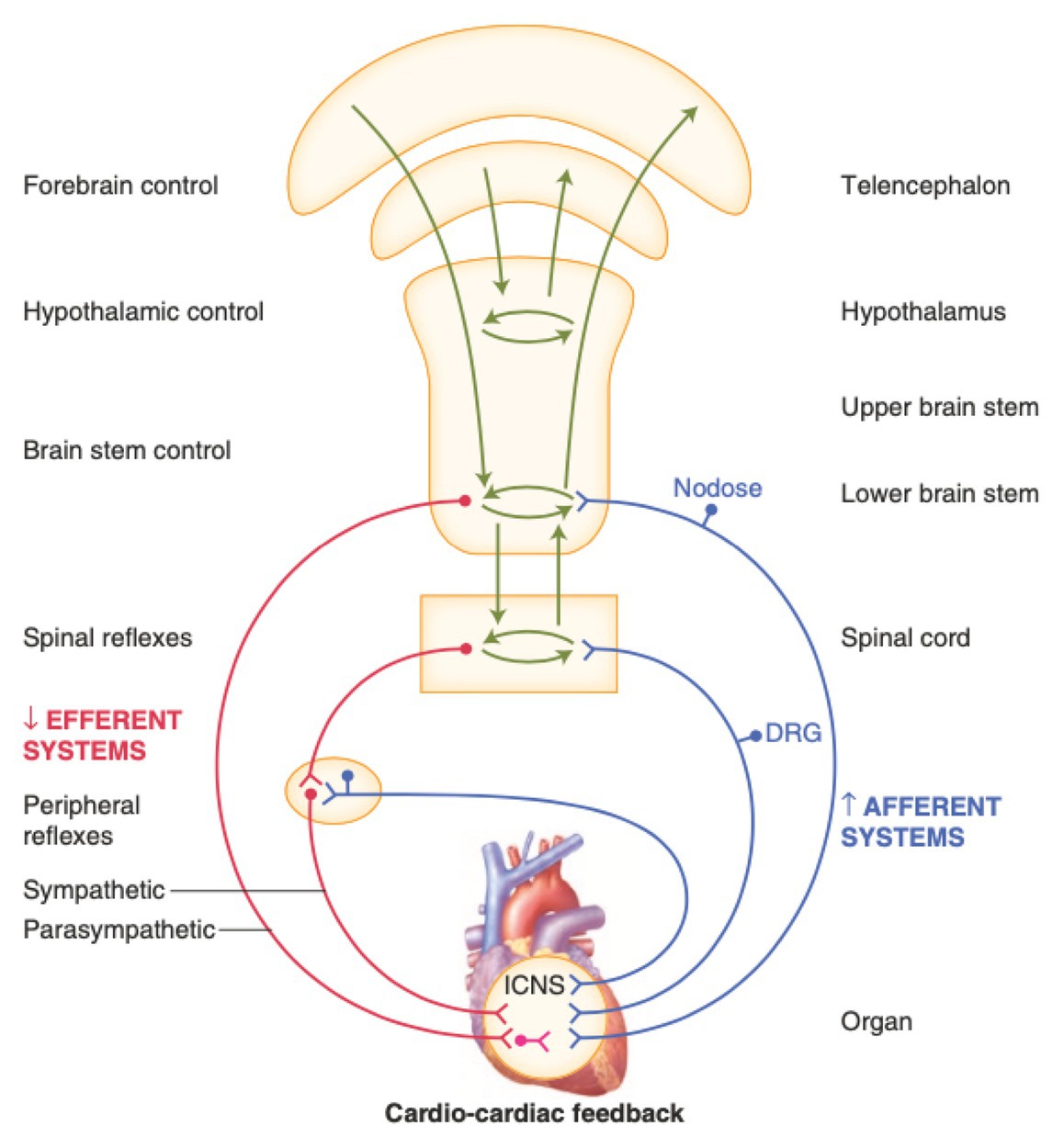
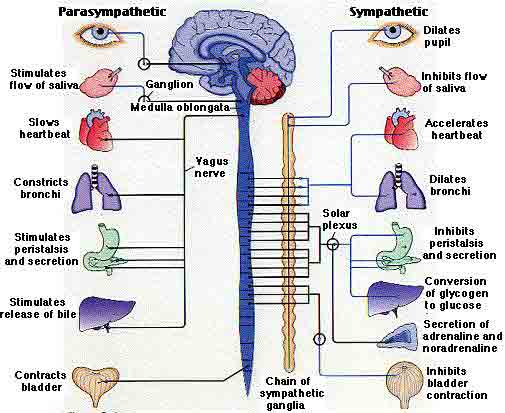
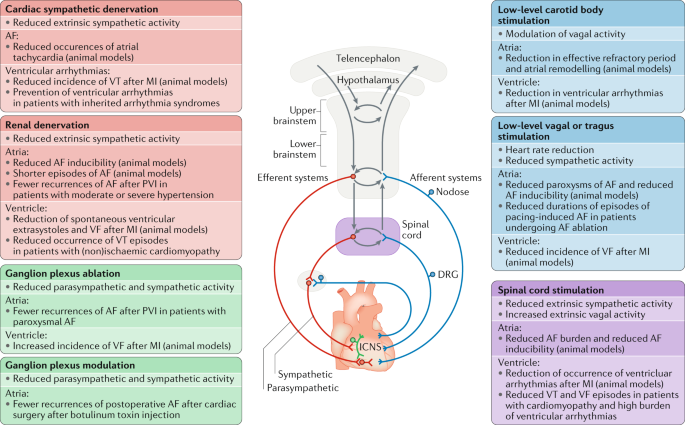
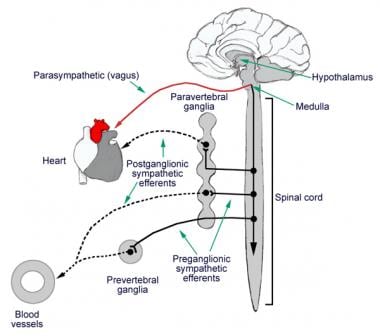
The kidney is both the contributing and the target organ of the hypertensive processes and the disease involves the interaction of multiple organ systems and numerous mechanisms of independent or interdependent pathways. The rate and force of contraction of the heart and the degree of constriction or dilatation of blood vessels are determined by the autonomic nervous system sympathetic and parasympathetic and hormones produced either by the heart and blood vessels ie paracrine or autocrine or at a distance from the heart and blood vessels ie endocrine.
Therefore incremental dosing is necessary.
Venous return refers to the flow of blood from the periphery back to the right atrium and except for periods of a few seconds it is equal to cardiac output. The acute phase is aimed at treating the congestion and supporting cardiac output. Venous return refers to the flow of blood from the periphery back to the right atrium and except for periods of a few seconds it is equal to cardiac output. The kidney is both the contributing and the target organ of the hypertensive processes and the disease involves the interaction of multiple organ systems and numerous mechanisms of independent or interdependent pathways. Because clinicians and investigators have long observed that factors affecting primarily the venous side of the circulation can have profound influence on cardiac output mechanisms governing the flow of blood to the heart. Dopamine constitutes about 80 of the catecholamine content in the brain. The pathogenesis of essential hypertension is multifactorial and highly complex. The heart rate can vary according to the bodys physical needs including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide but is also modulated by a myriad of factors including but not limited to genetics physical fitness stress or psychological status. Factors that play an important role in the.
The kidney is both the contributing and the target organ of the hypertensive processes and the disease involves the interaction of multiple organ systems and numerous mechanisms of independent or interdependent pathways. Dopamine constitutes about 80 of the catecholamine content in the brain. Heart rate is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions beats of the heart per minute bpm. As a result hypoxemia typically results in a fall in systemic vascular resistance SVR and increased sympathetic input both of which lead to increases in stroke volume heart rate and cardiac output. Dopamine DA a contraction of 34-dihydroxyphenethylamine is a neurotransmitter that plays several important roles in cells. Therefore incremental dosing is necessary. Because clinicians and investigators have long observed that factors affecting primarily the venous side of the circulation can have profound influence on cardiac output mechanisms governing the flow of blood to the heart.

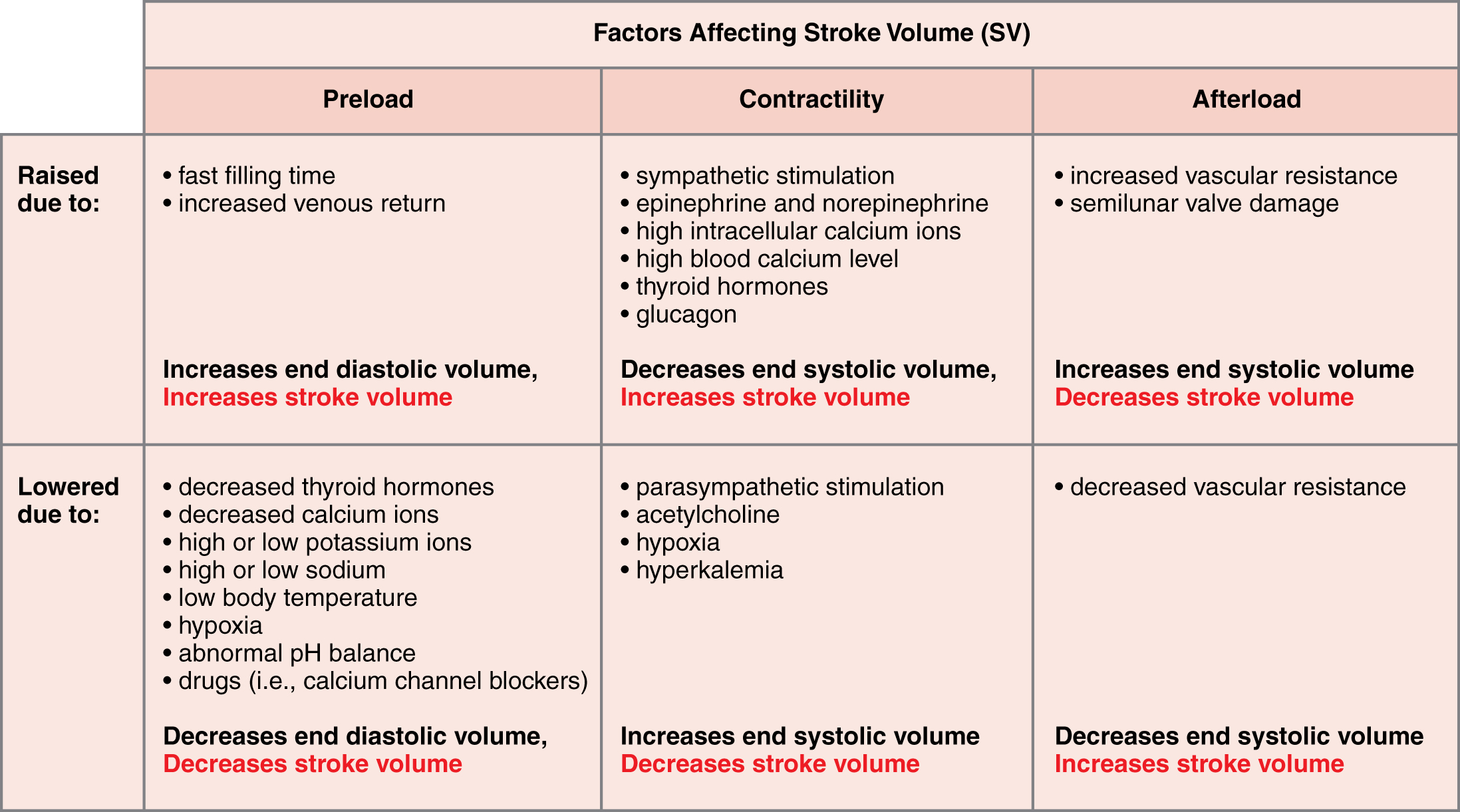








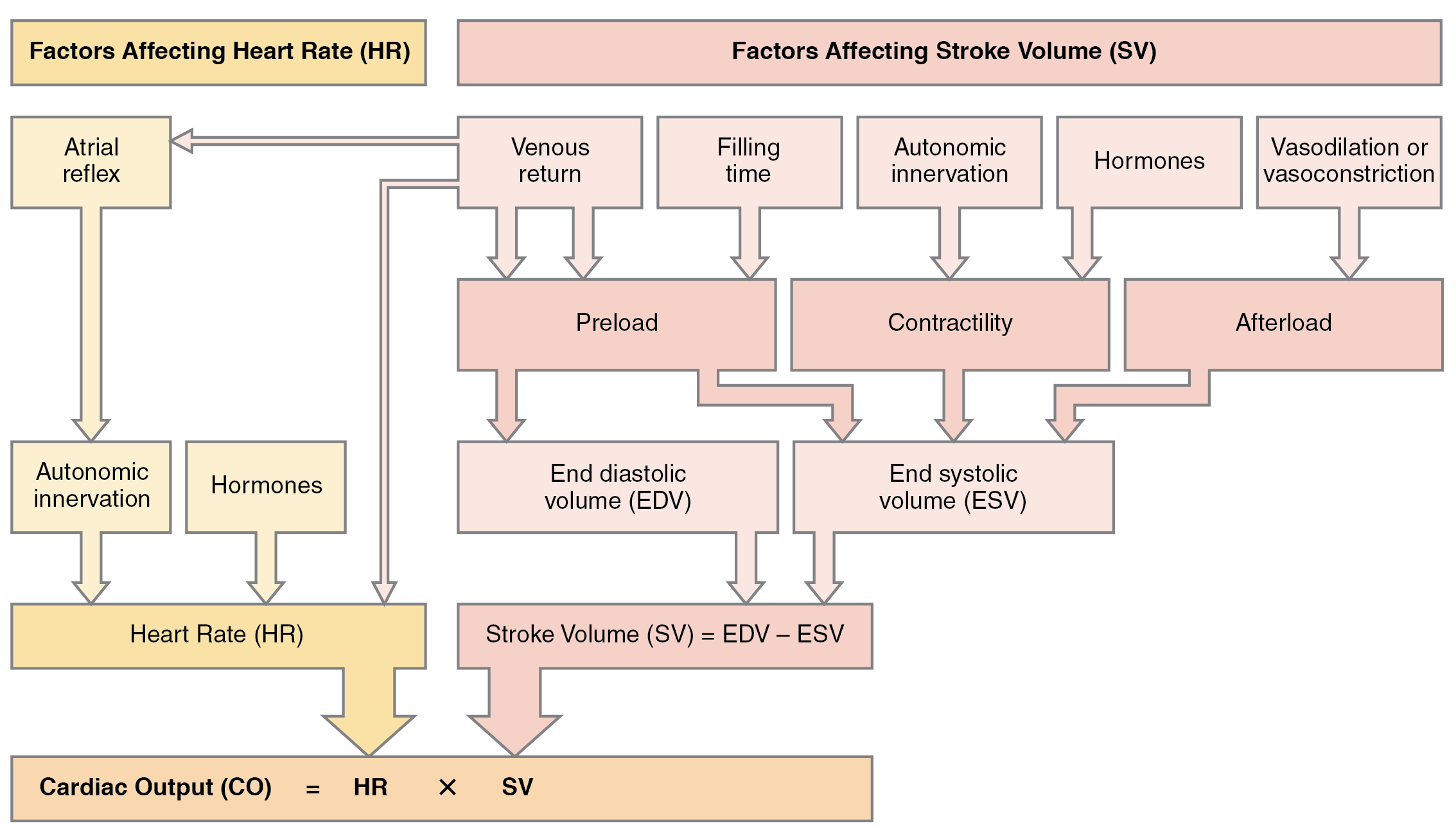




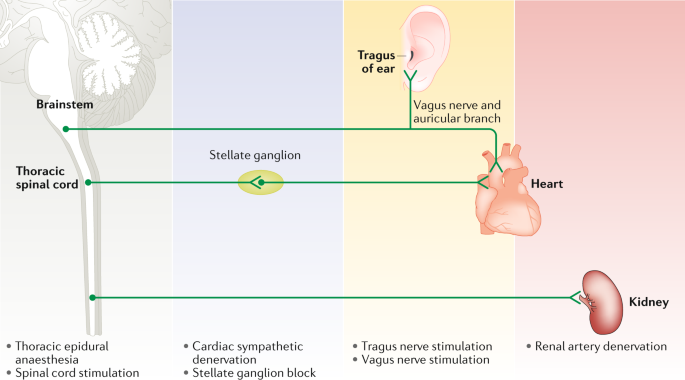
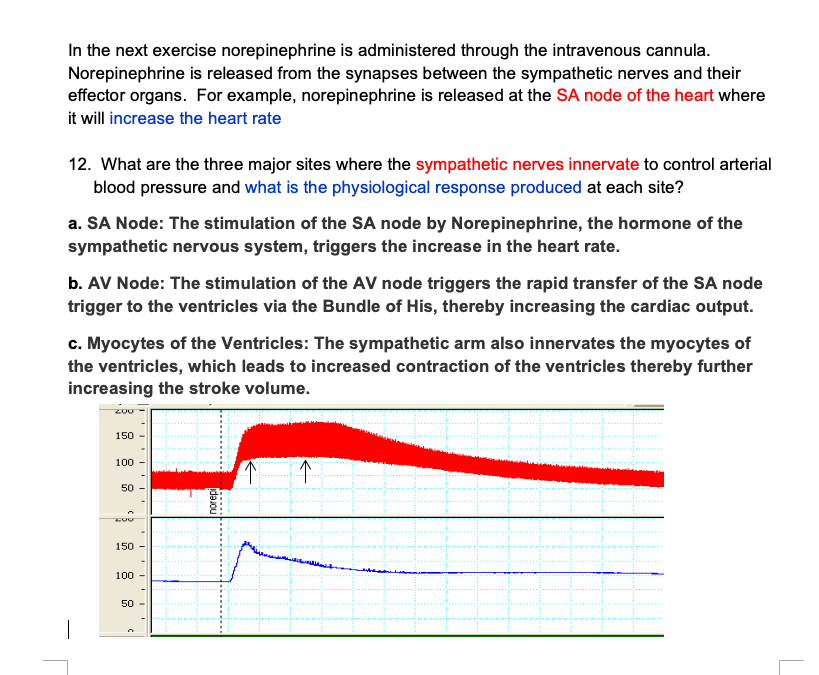


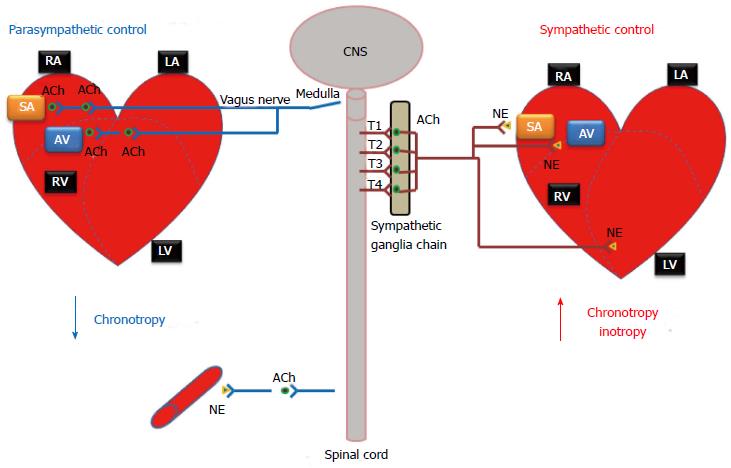
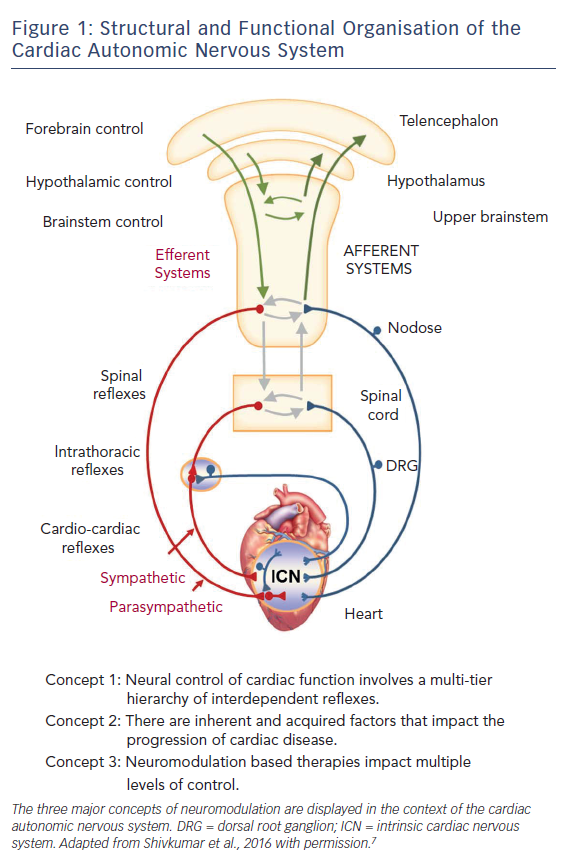

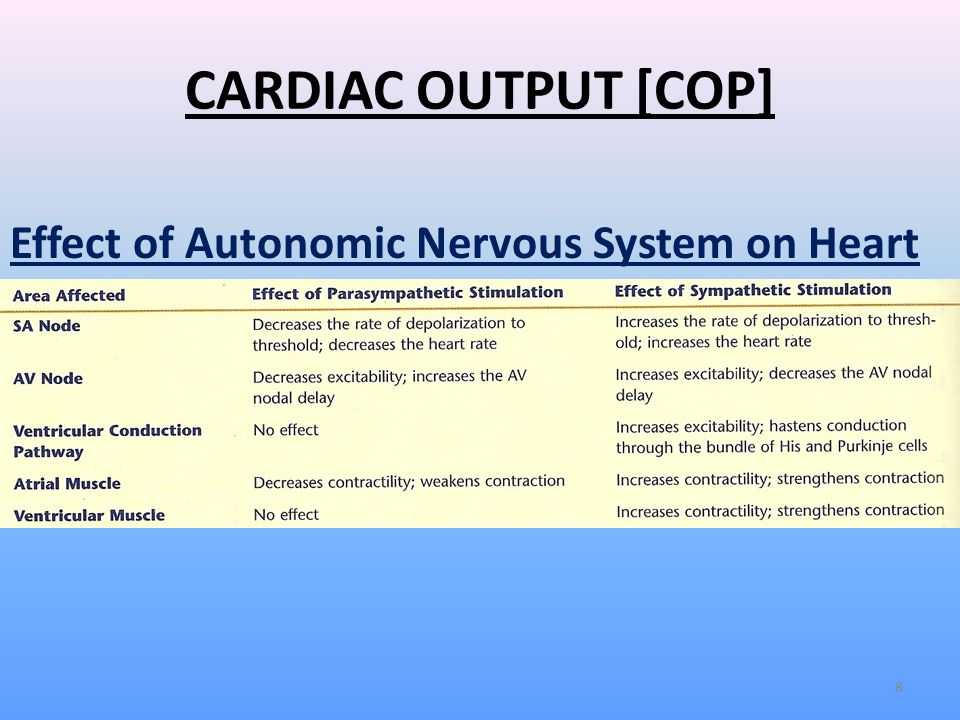

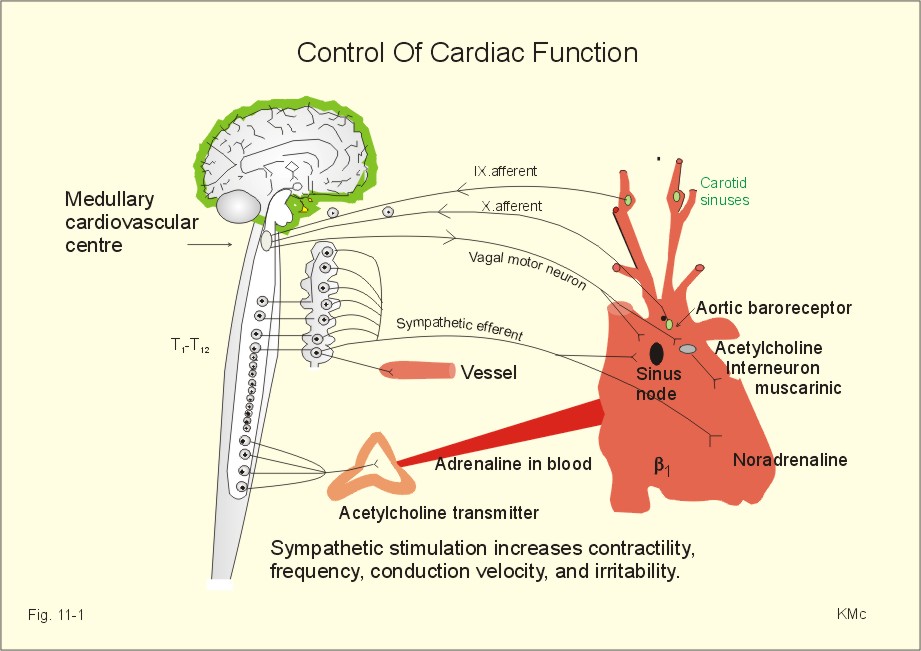















Post a Comment for "What Effect Does Sympathetic Nervous System Stimulation Of The Heart Have On Cardiac Output?"